Last Updated on January 22, 2023
Sometimes – the DM says, smugly – the destination is the journey.
While Dungeons & Dragons is ostensibly a game about descending into crypts, caves, and castles to fight monsters and (hopefully) make it out alive with as much shiny loot as you can carry, what about getting to the dungeon in the first place?
Whether you want your game of D&D 5e to feel like it’s taking place in a vast, living, breathing world where danger lurks around every tree or would rather sweep all that tedious mucking about in bandit-infested wilderness to one side and get right to the good stuff, all dungeon masters and players should at least give some thought to travel and how it works.
Welcome to our guide to traveling through the wilderness in D&D 5e.
This guide is going to break down how wilderness travel works, some of the different ways you can approach travel in your games, and some of the different types of maps dungeon masters can use to influence the way traveling through your world feels.
Note that while this guide touches on the concept of random encounters, that’s a much bigger can of purple worms than we have time to tackle in full today, so watch this space, I guess?
How Does Overland and Wilderness Travel Work in DnD 5e?

As with many elements of D&D 5e, the exact procedure for traveling through the wilderness is, ultimately, up to the DM.
And, as with all things left up to the DM, the only right answer is “whatever works for you, your players, and the type of campaign you want to run.”
Some DMs love a super-granular crawl through monster-infested forests and mountains, meticulously tracking rations, desperately foraging for nuts and berries, and spending nights huddled together, staring out into the gathering darkness for the telltale flash of a hungry monster’s eyes in the firelight.
Others choose to handwave travel completely.
Maybe running a wilderness survival simulator holds no interest, or perhaps they know they only have three hours to get through this dungeon before everyone has to go to bed, and they’ll be damned if the party spends two of those hours falling into swamps and getting chased up a tree by an angry owlbear.
To each their own.
Most games of D&D 5e tend to fall somewhere in the middle with the DM cherry-picking the travel rules that they find interesting or useful and skipping over the rest or perhaps choosing on a case-by-case basis.
An adventuring party’s first journey through a notoriously treacherous swamp might be fraught with peril, Survival checks, and wandering monsters.
By the time the party has leveled up, made the journey half a dozen times, and paid the local Baron to clear a road through the swamp, they may not have to roll at all.
Travel Pace in 5e
When walking across open ground, a party of characters can move at a normal, fast, or slow pace, which determines how far they can travel per day as well as how well equipped they are to spot potential threats.
| Pace | Distance per Minute | Distance per Hour | Distance per Day | Effect |
| Fast | 400 feet | 4 miles | 30 miles | -5 penalty to passive Wisdom (Perception) scores |
| Normal | 300 feet | 3 miles | 24 miles | – |
| Slow | 200 feet | 2 miles | 18 miles | Able to use stealth |
Adventurers can travel for up to eight hours per day; anything longer than that and you run the risk of accumulating levels of exhaustion. Deciding to continue for longer than eight hours is called a Forced March.
For each additional hour of travel beyond eight hours, the characters cover the distance shown in the Hour column for their pace.
However, at the end of each hour of travel beyond eight, each character must make a Constitution saving throw. The DC is 10 + 1 for each hour past eight hours. On a failed saving throw, a character suffers one level of exhaustion.
Marching Order
Whether you’re moving through cramped dungeon corridors or tracking a party of orcs across open plains, the DM may call on you to describe your party’s marching order.
This means you choose who walks in front; who’s second, third, etc.; and which character is bringing up the rear.
A party’s marching order usually determines who gets to make perception checks to notice things ahead of or behind the party.
The character (or characters, if there’s enough room for multiple adventurers to travel abreast) in the front rank usually makes Survival checks to navigate, detect approaching monsters, and spot hazards or traps.
If the party is being followed (or hunted), the character at the back is usually the one who makes the Perception check to notice.
Getting Lost
A party moving slowly is also less likely to become lost.
Whenever the DM decides that the party – because they were too cheap to hire a guide, neglected to buy a map, or are just somewhere that no one has ever been before – is running the risk of becoming lost, they can call on the party’s navigator (usually the character at the front of the marching order) to make a Survival check.
The DC is determined by the terrain through which the party is traveling.
| Terrain | DC |
| Forest, jungle, swamp, mountains, or open sea with overcast skies and no land in sight | 15 |
| Arctic, desert, hills, or open sea with clear skies and no land in sight | 10 |
| Grassland, meadow, farmland | 5 |
The check made by the party’s navigator is modified by the characters’ Travel Pace. A slow-moving party gets a +5 bonus to their Survival check, and a fast-moving party gets a -5 penalty.
Rangers: Natural Explorers in Their Favored Terrain
One of the best ways to mitigate the dangers of traveling through the wilderness is to make sure you have a ranger in your party – either by having one as a player character or hiring one as a retainer.
All rangers are familiar with one (or more) type of natural environment and gain a host of bonuses when traveling and surviving in that environment.
Rangers can choose a terrain from arctic, coast, desert, forest, grassland, mountain, swamp, or the Underdark.
While traveling in their favored terrain, rangers get expertise (doubling their proficiency bonus) when making Wisdom and Intelligence checks related to that environment as well as the following benefits:
- Difficult terrain doesn’t slow your group’s travel.
- Your group can’t become lost except by magical means.
- Even when you are engaged in another activity while traveling (such as foraging, navigating, or tracking), you remain alert to danger.
- If you are traveling alone, you can move stealthily at a normal pace.
- When you forage, you find twice as much food as you normally would.
- While tracking other creatures, you also learn their exact number, their sizes, and how long ago they passed through the area.
Traveling Over Difficult Terrain

The travel speeds listed above assume the characters are traveling over relatively unobstructed terrain like paved or dirt roads, rolling plains, or light forest.
However, traveling through difficult terrain, like swamps, thick forest, mountainous areas, or anywhere else where the going gets tough, halves your party’s movement speed in the same way that moving across difficult terrain during combat costs 2 feet of movement for every 1foot traveled.
Mounts and Vehicles
Mounts, like horses, camels, giant goats, or anything else your party’s +8 Animal Handling ranger can stick a saddle on, can travel at double walking speed for about an hour.
Anything beyond that and the mount needs to start making saving throws to avoid exhaustion.
Some mounts are specially adapted to their environments and, I would rule, negate any difficult terrain penalties imposed by their specific terrain.
A giant mountain goat mount, for example, would allow an adventurer to move through rocky, vertical terrain as though it were flat land. Need to get through a fetid swamp in a hurry? Did someone say riding alligators?
Animals can also be used to pull vehicles over land (and sometimes water – did someone say Alligator Water Chariot?).
While this is no quicker than walking, the benefit here is how much even a simple horse and cart can increase your carrying capacity.
An animal pulling a carriage, cart, chariot, sled, or wagon can move weight up to five times its base carrying capacity, including the weight of the vehicle.
If multiple animals pull the same vehicle, they can add their carrying capacity together.
Resting in the Wilderness
Apart from some edge cases like the warforged, all characters need to periodically take a rest, no matter if they’re topped up on hit points and spell slots.
During travel, it’s assumed that a party will need to take a short rest (one hour) every four hours, and a long rest (eight hours) at the end of eight hours of travel.
A party taking a long rest will also need to make camp as well as consume food and water in order to gain its benefits. In the wilderness, this can be easier said than done.
Foraging and Other Actions While Traveling
There are plenty of things your characters can (and probably should) do while traveling, including navigating, forage for food and water, map the surrounding area, and track creatures.
Usually, a party traveling slowly will do better at these activities, and a fast-moving party will act at a serious disadvantage.
Navigating not only helps you find your way to the journey’s destination, but also helps avoid environmental hazards, like quicksand, thin ice, or desecrated ground crawling with the undead, by making a Survival check.
Foraging allows you to find the food and water necessary for survival once your party’s rations run out.
A character who forages for food keeps their eyes peeled for vegetation, water sources, and game that can be hunted by making a Survival check. The DC of this check is set by the abundance of available food in the region.
| Food and Water Availability | DC |
| Abundant food and water sources | 10 |
| Limited food and water sources | 15 |
| Very little, if any, food and water sources | 20 |
Lush farmland and forests might yield an abundant supply of wild mushrooms, berries, fresh water, and rabbits to hunt.
By contrast, players trying to make their way through arctic tundra or scorching desert could end up going for days at a time without glimpsing the slightest trace of food or water.
Mapping the surrounding area involves a character taking the time to survey the surrounding landscape, noting down landmarks and geological features.
If the party later becomes lost (or travels through the same location later) a map can be a huge help in getting back on track.
Tracking quarry across the wilderness – whether the pursuit is the whole point of the journey or just a momentary diversion in search of food – relies on a player making one or more successful Survival checks.
The DM could set any number of DCs for the roll and require the player to roll multiple checks.
The difficulty of a check and the frequency with which the player has to roll could depend on any number of things, from the size of the quarry and the local terrain (tracking a giant’s progress through the forest requires little more than checking for huge footprints and broken branches and may not require a roll at all; following a displacer beast through its native jungle is a task so challenging that it verges on folly) to whether or not the party’s prey is aware of its pursuers.
A monster that’s just going about its business might only prompt a roll once per day, whereas a creature that’s actively trying to avoid detection could prompt a new roll each hour.

Weather
The weather is a vital consideration when moving through the wilderness. Climbing a mountain on a balmy summer afternoon is a very different prospect from attempting the same climb in the midst of a raging snowstorm.
The DM can either choose the weather to suit the environment and their campaign (trekking across cursed marshlands? It’s now raining frogs, which I guess eliminates the need for a foraging roll for the day) or roll on the table below.
| d20 | Temperature |
| 1–14 | Normal for the season |
| 15–17 | 1d4 × 10 degrees Fahrenheit colder than normal |
| 18–20 | 1d4 × 10 degrees Fahrenheit hotter than normal |
| d20 | Wind |
| 1–12 | None |
| 13–17 | Light |
| 18–20 | Strong |
| d20 | Precipitation |
| 1–12 | None |
| 13–17 | Light rain or light snowfall |
| 18–20 | Heavy rain or heavy snowfall |
Some DMs like to roll for weather changes as frequently as every hour, whereas some will just roll at the start of the day and let the result ride.
It’s also worth noting that some spells and character abilities, like Druidcraft, can allow characters to predict the weather as much as a day in advance.
Homebrewing the Wilderness
Plenty of DMs find the basic rules for weather (and wilderness travel in general) to be a little sparse. Thankfully, there are a ton of great options out there from the D&D community.
Try this free ruleset by KibblesTasty for a more in-depth set of options.
You should also check out Into the Wyrd and Wild by Wet Ink Games, which is absolutely overflowing with house rules for wilderness survival.
For the DM looking to make the wilderness into a truly scary place with lots of rich, rewarding gameplay, it’s got rules for weather, moon cycles, hunting and butchering monsters, and a whole bunch of super creepy monsters, spells, items and wilderness locations.
Definitely recommended.

Montages vs. Detailed Travel – Which One To Use and When
When running a journey through the wilderness, whether that means a week-long trek through a dark forest, scaling a mountain, or journeying through a vast cavern complex, the dungeon master has to decide whether they want to handwave the entire process, run a punishing test of survival over multiple sessions, or pick something somewhere in between.
The Dungeon Master’s Guide offers two suggestions for running wilderness and overland travel: the montage and the hour-by-hour approach.
Using a montage – like in film and TV – allows you to effectively gloss over large chunks of time while still reminding your players that their characters are undergoing a much more grueling time than sitting around the gaming table with a bag of chips and some Code Red Mountain Dew.
In a few sentences, you can describe sweeping vistas, moody forests, and the day-to-day experiences of the adventurers.
Just remember that no matter how much you’d rather be down in the dungeon throwing waves of goblins at your players, nailing a few key details of your montage can do a lot to help make your world feel real and evocative to your players.
While saying “you walk for three uneventful days” is perfectly serviceable, I guarantee that a few well-chosen sensory details are going to do a lot to help reinforce the fiction for your players.
Instead, try…
“You trudge for three days through driving rain and bitter cold, your breath rising in plumes before your faces. Your nights are spent huddled beneath what sparse cover you can find in these accursed hills, watching the darkness for signs of goblins – or worse.
The way is hard, rising again and again in a series of switchbacks and sharp doglegs as you venture deeper into the mountains. On the evening of the third day, tired, hungry, soaking wet, you arrive at your destination.”
Sure, it takes maybe 60 seconds longer, but your players are much more likely to feel immersed in the events. The wilderness feels more real to them now, and they’re more likely to play their characters accordingly.
If you (and your players) like wilderness travel, then using the rules in the previous sections to run the game hour-by-hour is a great way to go.
If you don’t want to get quite so nitty-gritty with it, you can always run each day in four-hour chunks, called “watches.”
Just like a montage, however, make sure that you hit a few sensory descriptors with each change in weather, terrain, and time of day.
These help orient your players and mitigate the risk that travel can start to feel a little too much like a board game – which, interestingly enough, it was in 1st edition D&D.
You actually had to buy a totally unrelated board game (which you can still find online if you’re into that sort of thing) that wasn’t even made by TSR, which you played instead of D&D until your characters reached the dungeon.
Random Encounters
We’ll go into random encounters in detail in a future article, but in essence, as you travel through the wilderness, random encounters simulate the chances of bumping into its various occupants.
The DM sets an increment of time (some use every hour, some use four, and some just roll once or twice per day) and rolls a d20 whenever their chosen duration is up.
If the result is a 19 or 20, then the players have a random encounter.
Random encounters can range from randomly determined monsters going about their business to friendly NPCs or even hooks to new adventures, depending on what the DM chooses to generate.
Adventurers moving at a fast pace are more likely to be surprised by a random encounter, and a slow-moving party will usually have a chance to stealth around it or lay an ambush if they choose.
Mapping the Wilderness
Lastly, we’re going to take a look at some of the ways to map the wilderness.

“Freestyle” Travel
This is probably the simplest option for dungeon masters who want to gloss over wilderness travel – especially when the players’ destination and the intervening lands are well known to them.
Freestyle mapping involves looking at the party’s location on your world or area map, plotting how far it is away from their intended destination in miles, and using their travel pace to figure out how many hours, days, or weeks the journey will take.
Maybe make note of the points at which they’ll pass by any other landmarks so you can describe them, and you’re good to go.
Hex Crawls
The “classic” flavor of D&D map, and ideal for games that focus on exploration and a more involved approach to wilderness travel.
A hex-map breaks up the world into six-sided spaces, which tend to be either 1 mile, 6 miles (the classic scale for a hex crawl), or larger for world maps.
Some hexes contain pre-written content, and entering an empty hex usually prompts a roll for a random encounter. Players then have the option of taking an action to explore, forage, or map their current hex or move on.
My favorite thing about hex crawls is that when the players get lost, you can roll a d6 and count round their current hex to determine the direction in which they move.
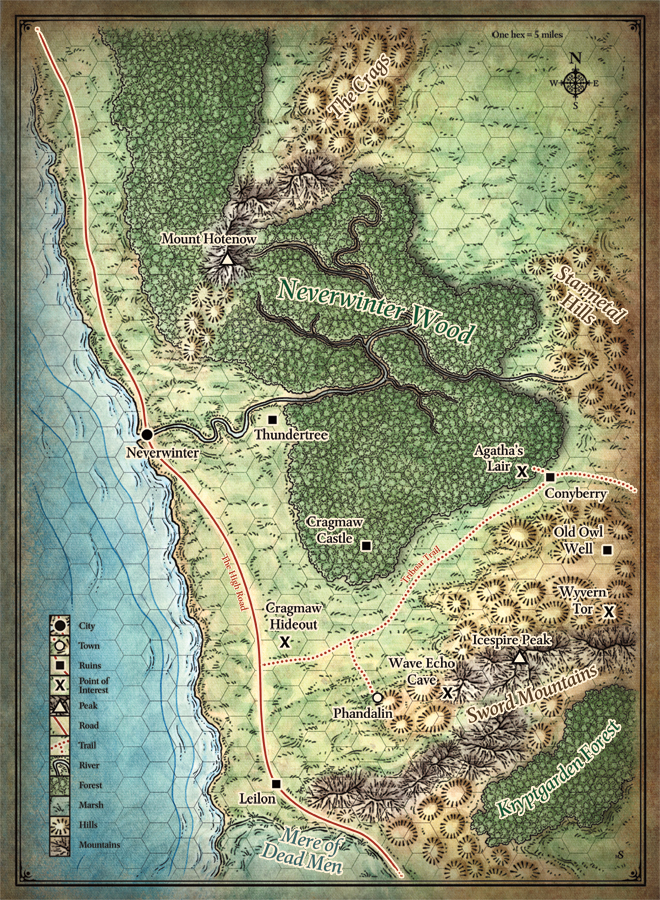
Point Crawls
This is a slightly more abstracted version of a hex crawl that has found favor with DMs looking to emphasize more liminal or unmappable environments.
Point Crawls contain several “points” of interest, which could be towns, dungeons, or other landmarks, with lines drawn between them marking out the distance and time required to make that journey.
When the party travels between two points, they could elect to travel any way they like – road, off-piste, or by flying golden barge, and the method of travel is then used to modify their expected travel time.
If you like the idea of including wilderness travel in your game but don’t want to muck about poring over maps to figure out if that tiny drawing of a hill would count as difficult terrain, the mixture of abstraction and mechanical crunch that point crawls provide might be for you.
- About Author
- Latest Posts
I played my first tabletop RPG (Pathfinder 1e, specifically) in college. I rocked up late to the first session with an unread rulebook and a human bard called Nick Jugger. It was a rocky start but I had a blast and now, the better part of a decade later, I play, write, and write about tabletop RPGs (mostly 5e, but also PBtA, Forged in the Dark and OSR) games for a living, which is wild.

I am creating a home brew campaign and would like to DM it for folks who enjoy outdoors, hiking, adventure, survival, etc. Leaning it heavier on teh description of the day to day, flora and fauna and terrain, weather, season, etc when applicable to play and journey. Your material will be very helpful. I also recently supported a Kickstarter for Into the Wild which I think will also be a very good resource.
I also happen to be a publisher and am curious if you have plans to collect your material into a book. I think it would be a swell idea . . . I could help, consult on, or partner with you on it. I need to read more of your articles.
Thank you,
David Martin
[email protected]